Science, Culture and Art
The cultural heritage of Russia is nothing short of remarkable in its richness and diversity. Our country has gifted the world with brilliant composers, artists, and writers.
For many centuries, Russian scientists have made an invaluable contribution to the development of world science; their developments and discoveries advance the scientific and technical process and bring comfort to everyday life.
Science
Russian scientific discoveries and innovative developments continue to drive global science forward. Many fundamental laws of nature were discovered by Russian scientists, and Russian technological inventions are used all over the world. Russia is well known for its technological breakthroughs and achievements—one of the most famous being the first human spaceflight.
The field of information technology is highly developed in Russia. Russian specialists, who have introduced groundbreaking developments in cybersecurity, consistently rank high in global ratings.
In addition, Russia offers vast opportunities for realizing scientific potential. The country is home to numerous research institutes, universities, and laboratories conducting studies in various scientific fields. A significant step in supporting scientific activity was the directive from Russian President Vladimir Putin to increase science funding to 2% of GDP by 2030. This initiative aims to not only strengthen Russia’s position in the international scientific community but also create favorable conditions for the development of new technologies and innovative solutions.
Famous Russian Scientists and Their Discoveries
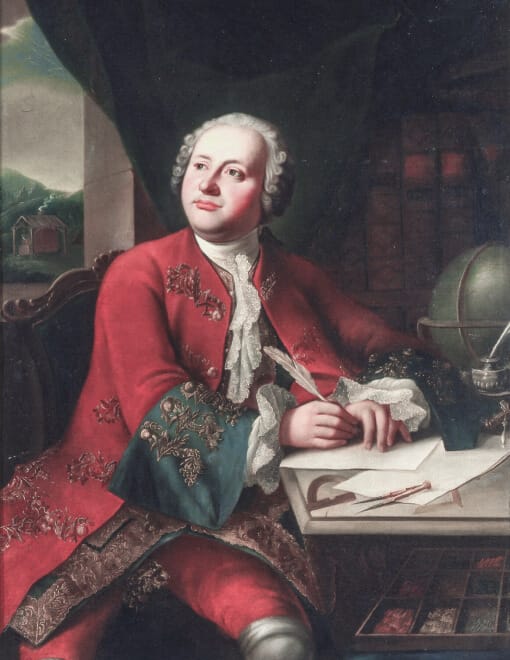
Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov
Lomonosov was the first Russian encyclopedic scientist who made significant contributions to both the humanities and natural sciences. As a member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, he played a crucial role in the development of Russian science.
One of his major contributions was the creation of Russian Grammar, which became the foundation for the study of the Russian language and its rules. He is also known as the founder of the anti-Normanist theory, arguing that Ancient Rus was not formed under Norman influence but emerged through the internal development of Slavic peoples.
In natural sciences, Lomonosov formulated the universal law of conservation of matter and motion, which became fundamental in physics, and developed the molecular-kinetic theory of heat, explaining the nature of thermal phenomena and molecular interactions.

Nikolai Ivanovich Pirogov
A Russian surgeon, anatomist, and educator, Pirogov had a profound impact on the development of surgery and medicine in Russia and beyond. He was one of the founders of field surgery and is considered the father of military field surgery due to his introduction of new methods for treating the wounded during the Crimean War.
Pirogov is also known as the creator of the world’s first atlas of topographical anatomy, which became an essential tool for surgeons and anatomists. The atlas included detailed anatomical drawings, significantly improving the understanding of human anatomy and enhancing surgical safety.
He was the first in Russia to perform surgery using anesthesia, marking a major advancement in surgical practice. Pirogov was a corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences and left a rich medical legacy that continues to influence modern surgery.
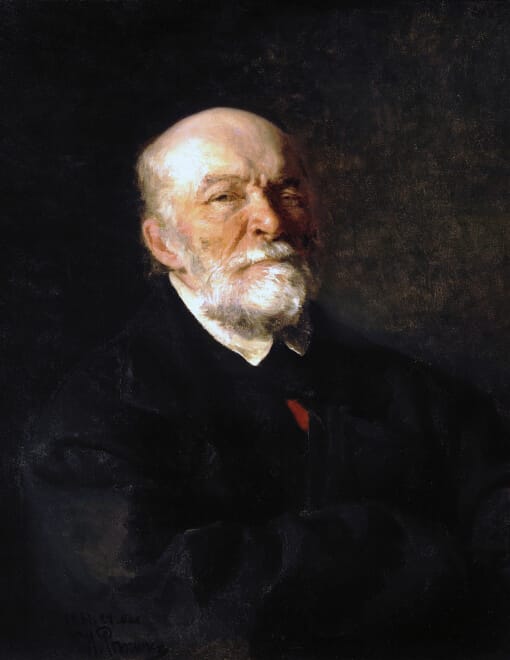
Sergei Petrovich Botkin
A Russian physician and founder of the clinical school of medicine, Botkin was one of the most influential medical figures of his time. He played a key role in developing clinical medicine in Russia and became known for his research in epidemiology.
Botkin studied the spread of infectious diseases such as cholera, plague, typhus, and diphtheria. His work improved diagnostic and treatment methods and helped form more effective epidemic control strategies.
He was the first Russian court physician to the imperial family, influencing medical practices at the highest levels. In 1861, Botkin opened the first outpatient clinic in Russia where treatment was provided free of charge, making healthcare more accessible and marking a milestone in the development of the country's healthcare system.
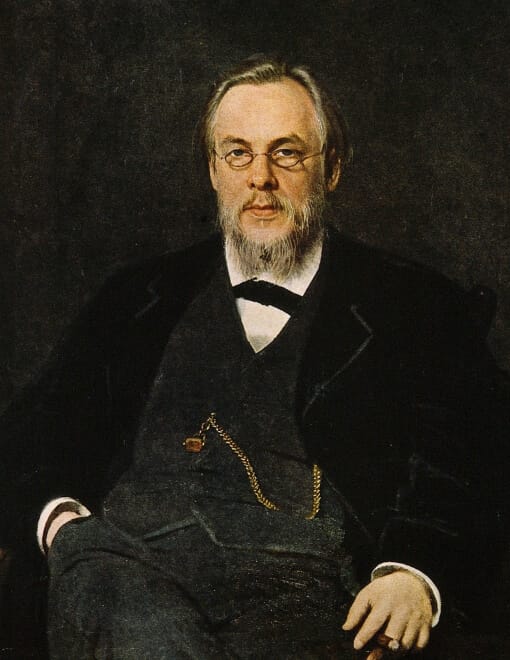

Pavel Nikolaevich Yablochkov
A Russian inventor, electrical engineer, and technician, Yablochkov is best known for inventing the arc lamp, known as the Yablochkov Candle, in 1876. This was one of the first commercially successful electric light sources.
He also developed a system that allowed many electric lamps to be powered from a single generator, which significantly simplified and reduced the cost of electric lighting. This was especially useful in public places and industrial settings.
Yablochkov actively promoted electric lighting in Russia and abroad. He showcased his inventions at the 1878 World's Fair in Paris, where his work received great attention and acclaim.
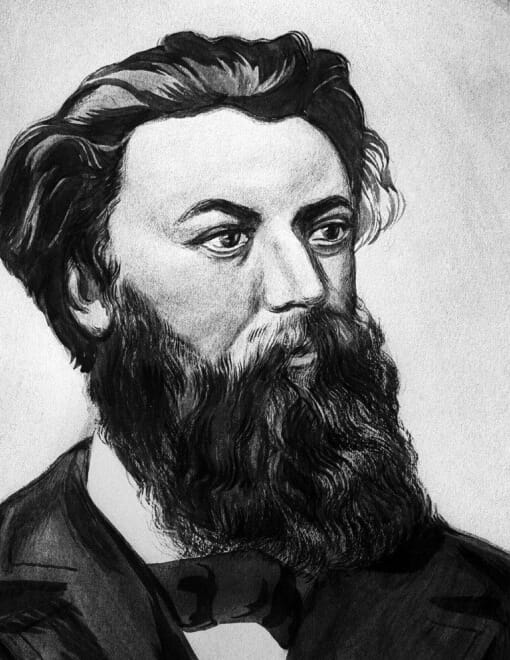

Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky
Regarded as the father of Russian and Soviet astronautics, Tsiolkovsky was a pioneering scientist and inventor in aerodynamics and aviation.
In 1897, he built the first wind tunnel in Russia, allowing experiments with aircraft models under conditions close to real flight.
In 1903, he proved that rockets could overcome Earth’s gravity and reach outer space using the principle of reactive motion. His ideas on multistage rockets and liquid-fuel propulsion became the foundation for future developments in rocket science.
Tsiolkovsky’s work had a major influence on the progress of rocket engineering both in Russia and internationally. Numerous objects — including spacecraft, scientific institutions, and even a lunar crater — are named in his honor.


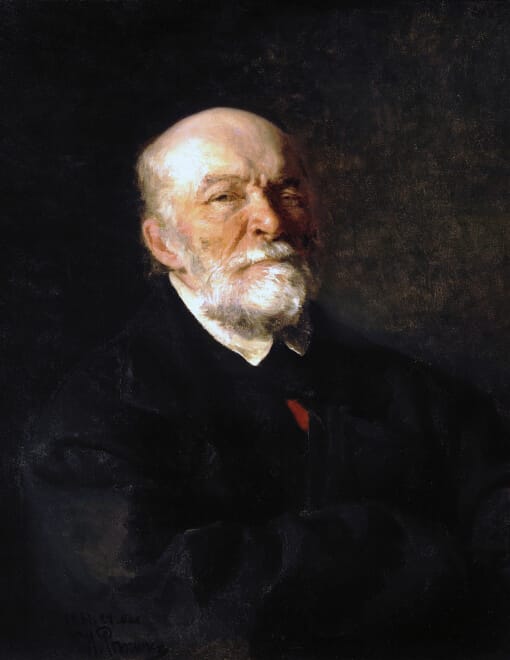



Folk Culture
Russia is famous for its great artists and architects. Russian artists have created many paintings recognized worldwide. The architecture of Russian cities impresses with its solemnity, monumentality, and at the same time, elegance: here, monuments of traditional Russian architecture harmoniously coexist with intricately designed Baroque palaces and grandiose buildings of the 20th century.
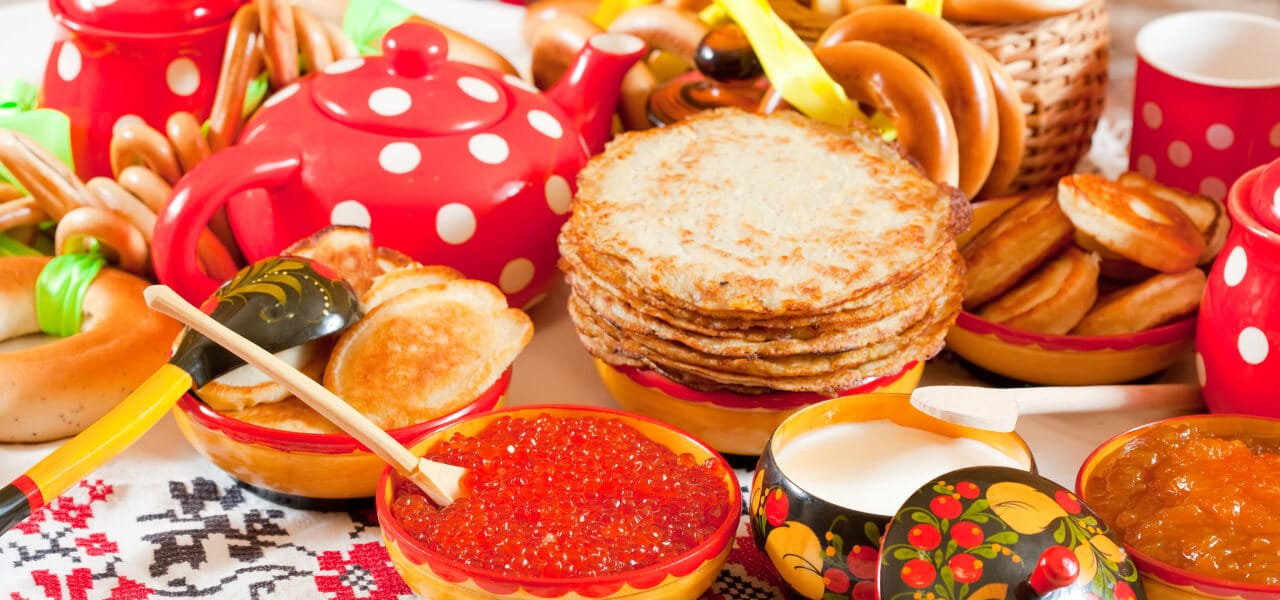

There are many folk crafts and trades in Russia. Traditional Russian patterns, embroidery, wood carving, and clay and ceramic pottery are just a few examples of unique crafts passed down from generation to generation.
Another important aspect of Russia's folk culture is national clothing. The diversity of traditional costumes in different regions of Russia reflects the uniqueness of each people and their historical path. Kokoshniks, sarafans, hats and lapti are just a few elements of the recognizable Russian style.
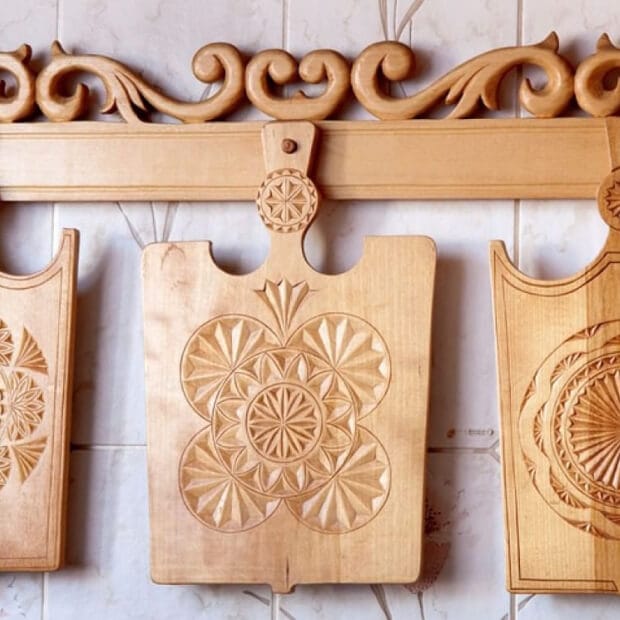
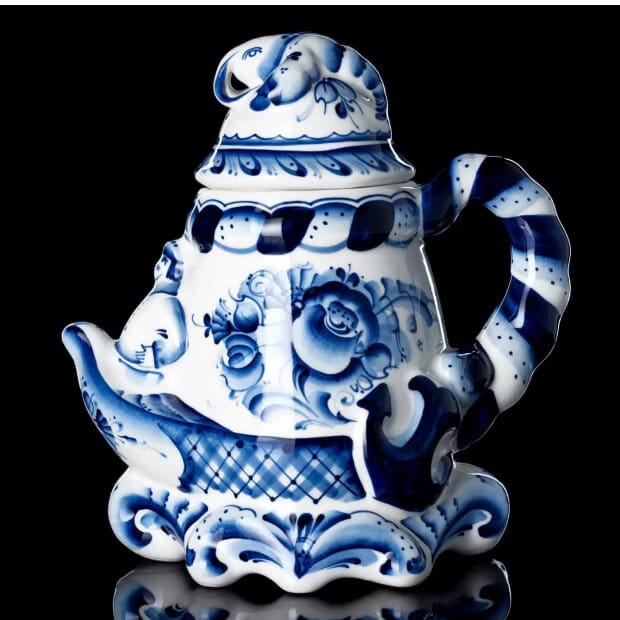


Folk culture in Russia continues to be preserved and developed today, thanks to the efforts of folk groups, both professional and amateur. Festivals of folk art, celebrations, exhibitions, and concerts are vibrant events where one can experience the amazing atmosphere of Russian culture. The folk culture of Russia is a priceless treasure that reflects the national dignity and centuries-old history of the country. It represents a unique combination of diverse traditions, customs, and crafts that make Russia special and distinctive.
Art
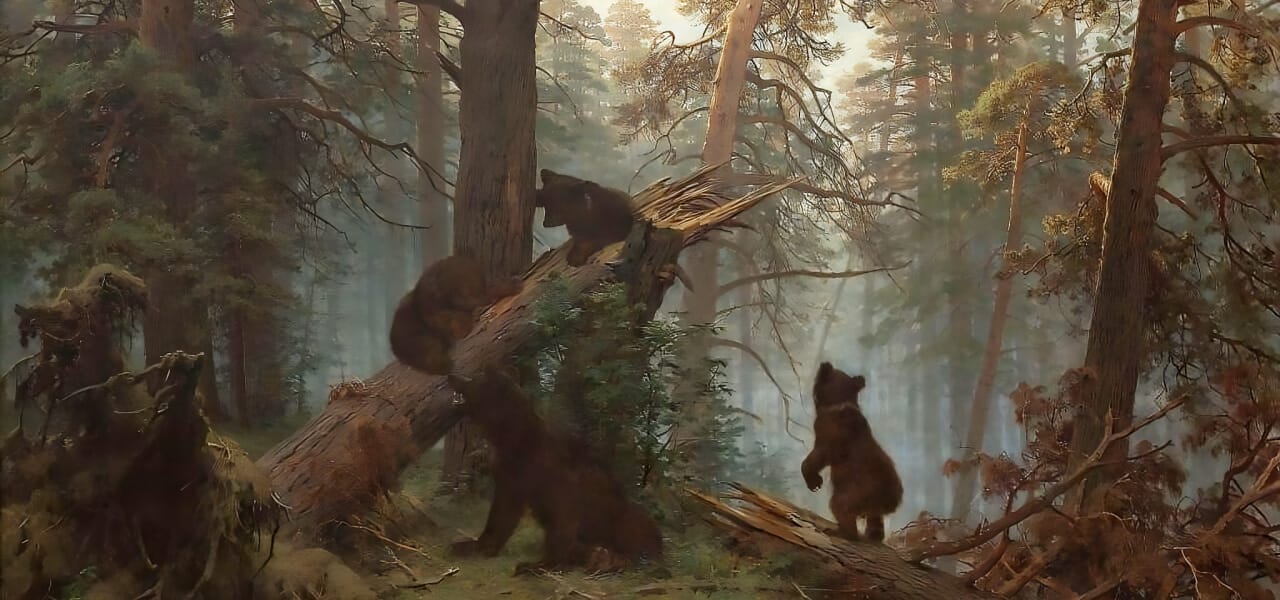
Russia is famous for its great artists and architects. Russian artists have painted many world-famous paintings. The architecture of Russian cities impresses with its solemnity, monumentality, and at the same time, elegance: here, monuments of traditional Russian architecture harmoniously coexist with intricately designed Baroque palaces and grandiose buildings of the 20th century.

Music
Russia is the homeland of many world-renowned composers. Many famous symphonies, operas, and ballets have been created by our authors. Russian classical music is characterized by its originality and unique grandeur, and even today, the works of our composers sound modern. The folk music of our country is also not forgotten: many songs are still well-known and loved by Russians.
